Unlocking the Power of Enterprise Architecture: A Guide to Success
Introduction
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on unlocking the power of enterprise architecture. In today's fast-paced business world, organizations are constantly looking for ways to maximize efficiency, streamline operations, and drive innovation. This is where enterprise architecture comes into play. By providing a holistic view of an organization's structure, processes, systems, and technology, enterprise architecture enables businesses to align their strategies and goals with their IT capabilities.
In this guide, we will delve deep into the world of enterprise architecture, exploring its key concepts, benefits, and implementation strategies. We will also discuss the role of solution architecture management in driving successful enterprise architecture initiatives. So let's get started on our journey to unlock the power of enterprise architecture!
Table of Contents
What is Enterprise Architecture?
Enterprise architecture can be defined as a strategic framework that helps organizations align their business objectives with their IT capabilities in order to achieve optimal performance and competitive advantage.
At its core, enterprise architecture focuses on understanding the current state and future vision of an organization's structure, processes, systems, and technology landscape. It provides a blueprint that guides decision-making and investment in IT resources, ensuring that they are aligned with the organization's goals and objectives.
The Importance of Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture plays a crucial role in the success of any organization. It provides a structured approach to managing complexity and enables businesses to:
Improve Decision Making: By providing a holistic view of an organization's operations, enterprise architecture helps decision-makers understand the impact of their decisions on various business functions and IT systems.
Drive Innovation: Enterprise architecture facilitates innovation by identifying areas of improvement and enabling the development and implementation of new technologies and processes.
Enhance Agility: In today's rapidly changing business landscape, organizations need to be agile and responsive to market dynamics. Enterprise architecture enables businesses to quickly adapt to changes by aligning their IT capabilities with their strategic goals.
Reduce Costs: By optimizing IT resources and eliminating redundancies, enterprise architecture helps organizations reduce costs associated with IT infrastructure and operations.
Ensure Compliance: Enterprise architecture provides a framework for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices.
Key Components of Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture comprises several key components that collectively provide a comprehensive view of an organization's structure and capabilities. These components include:
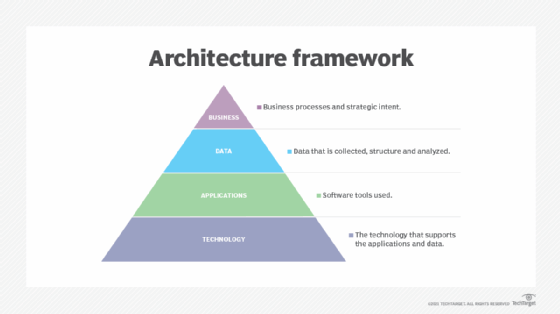
Business Architecture: This component focuses on understanding the organization's business strategy, goals, processes, and organizational structure. It defines the key business functions, capabilities, and relationships that drive value creation.
Information Architecture: Information architecture deals with the management and governance of data within an organization. It includes data models, data dictionaries, data integration strategies, and data quality frameworks.
Application Architecture: Application architecture focuses on the design and integration of software applications within an organization's IT landscape. It includes the identification of application components, interfaces, dependencies, and integration patterns.
Technology Architecture: Technology architecture deals with the selection, deployment, and management of technology infrastructure within an organization. It includes hardware, software, networks, and security components.
Benefits of Adopting Enterprise Architecture
The adoption of enterprise architecture offers several benefits to organizations. Some of the key benefits include:
Improved Alignment: Enterprise architecture ensures that IT investments are aligned with business goals and objectives, enabling organizations to achieve better outcomes.
Enhanced Efficiency: By identifying redundancies and streamlining processes, enterprise architecture improves operational efficiency and reduces costs.
Effective Decision Making: Enterprise architecture provides decision-makers with timely and accurate information, enabling them to make informed decisions that drive business success.
Increased Agility: With a clear understanding of their IT capabilities, organizations can quickly respond to market changes and seize new opportunities.
Better Risk Management: Enterprise architecture helps organizations identify and mitigate risks associated with IT investments, ensuring that they are in line with industry standards and best practices.
Improved Collaboration: Enterprise architecture fosters collaboration among different stakeholders by providing a common language and framework for communication.
Challenges in Implementing Enterprise Architecture
Implementing enterprise architecture is not without its challenges. Some of the common challenges organizations face include:
Lack of Executive Support: Successful implementation of enterprise architecture requires strong executive sponsorship and support. Without this support, it can be challenging to secure the necessary resources and overcome resistance to change.
Organizational Silos: In many organizations, different departments operate in silos with limited collaboration. This can hinder the effective implementation of enterprise architecture as it requires cross-functional coordination and cooperation.
Resistance to Change: Change is often met with resistance, especially when it involves altering existing processes or systems. Overcoming resistance to change is critical for the successful implementation of enterprise architecture.
Complexity: Enterprise architecture initiatives can be complex due to the large number of stakeholders involved, the diverse nature of IT systems, and the need for ongoing maintenance and updates.
Lack of Skills and Expertise: Implementing enterprise architecture requires specialized skills and expertise. Organizations may need to invest in training or hire external consultants to bridge the skills gap.
Best Practices for Successful Enterprise Architecture Adoption
To ensure the successful adoption of enterprise architecture, organizations can follow these best practices:
Secure Executive Support: Securing executive support is crucial for the success of any enterprise architecture initiative. Executives can provide the necessary resources, overcome barriers, and drive organizational change.
Define a Clear Vision and Strategy: Organizations should define a clear vision and strategy for their enterprise architecture initiatives. This includes identifying key goals, objectives, and expected outcomes.
Engage Stakeholders: Engaging stakeholders from different parts of the organization is essential for successful enterprise architecture adoption. This includes involving business leaders, IT professionals, and end-users in the decision-making process.
Start Small and Scale Up: Implementing enterprise architecture can be a complex process. Starting small with a pilot project allows organizations to test the effectiveness of their approach before scaling up.
Leverage Existing Standards and Frameworks: There are several established standards and frameworks available for enterprise architecture implementation, such as TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) and Zachman Framework. Leveraging these frameworks can help organizations streamline their efforts.
Continuously Monitor and Adapt: Enterprise architecture is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Organizations should continuously monitor their architecture landscape, adapt to changing business needs, and update their strategies accordingly.
Understanding Solution Architecture
Solution architecture is a subset of enterprise architecture that focuses on designing specific solutions to address business problems or meet specific business requirements. It involves defining the structure, behavior, and characteristics of individual solutions within the broader context of the organization's overall architecture.
A solution architect is responsible for translating business requirements into technical specifications, ensuring that the solution aligns with the organization's enterprise architecture principles and standards. They work closely with stakeholders, including business analysts, developers, and project managers, to deliver high-quality solutions that meet business needs.
The Role of Solution Architects
Solution architects play a critical role in the success of enterprise architecture initiatives. Some of their key responsibilities include:
Requirements Analysis: Solution architects work closely with business stakeholders to understand their requirements and translate them into technical specifications.
Designing Solutions: Solution architects design solutions that meet business requirements while adhering to the organization's enterprise architecture principles and standards.
Technical Leadership: Solution architects provide technical leadership to development teams, ensuring that solutions are implemented correctly and efficiently.
Managing Risks: Solution architects identify potential risks and issues associated with solution implementation and propose mitigation strategies.
Collaboration: Solution architects collaborate with various stakeholders, including business analysts, developers, and project managers, to ensure successful solution delivery.
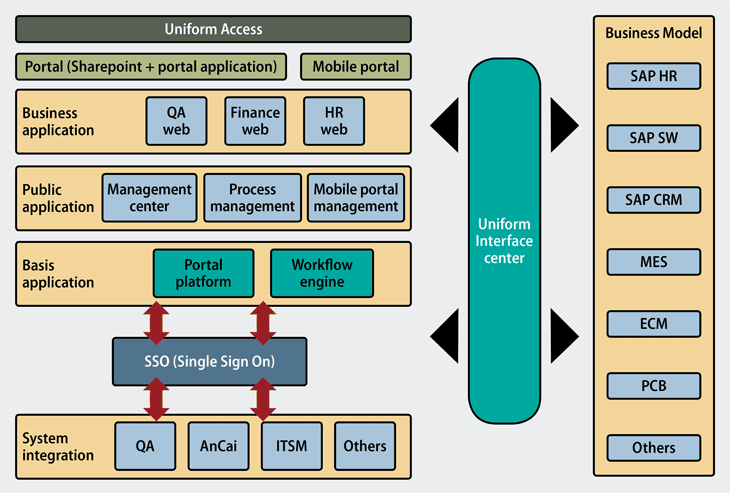
Leveraging Enterprise Architecture Tools
Enterprise architecture tools play a crucial role in simplifying and streamlining the enterprise architecture process. These tools provide a platform for capturing, modeling, analyzing, and managing enterprise architecture artifacts.
Some popular enterprise architecture tools include:
Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect: Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect is a comprehensive modeling tool that supports all aspects of enterprise architecture development. It allows organizations to create architectural models, capture requirements, analyze dependencies, and generate reports.
IBM Rational Software Architect: IBM Rational Software Architect provides a collaborative development environment for designing software architectures. It supports various modeling languages and allows organizations to visualize, document, and analyze their architectures.
Mega HOPEX: Mega HOPEX is an integrated suite of software solutions for enterprise architecture management. It provides capabilities for modeling, analyzing, planning, and implementing enterprise architectures.
ARIS Architect & Designer: ARIS Architect & Designer is a powerful enterprise architecture tool that enables organizations to model, analyze, and optimize their business processes. It supports various modeling languages and provides advanced analytics and reporting capabilities.
By leveraging these tools, organizations can streamline their enterprise architecture efforts, enhance collaboration among stakeholders, and improve Click here to find out more decision-making.
An Overview of Application Portfolio Management (APM)
Application Portfolio Management (APM) is a discipline within enterprise architecture that focuses on managing an organization's portfolio of applications. APM involves the identification, analysis, and optimization of applications to ensure that they align with business goals and objectives.
The key objectives of APM include:
Rationalizing the Application Portfolio: APM helps organizations identify redundant or underperforming applications and make informed decisions about retiring, replacing, or consolidating them.
Aligning Applications with Business Strategy: APM ensures that the application portfolio is aligned with the organization's business strategy and goals. This includes identifying gaps in functionality, identifying opportunities for improvement, and prioritizing investments.
Optimizing Costs: APM helps organizations optimize costs associated with application maintenance, licensing, support, and infrastructure.
Managing Risk: APM enables organizations to identify potential risks associated with applications and develop strategies for mitigating them. This includes assessing security vulnerabilities, compliance issues, and dependencies on unsupported technologies.
Streamlining APM with ServiceNow Application Portfolio Management (APM) Tools
ServiceNow offers a comprehensive suite of application portfolio management (APM) tools that enable organizations to streamline their APM efforts. These tools provide capabilities for capturing application inventory data, analyzing application portfolios, assessing application health and risk, and making informed decisions about application rationalization.
Some key features of ServiceNow APM tools include:
Application Inventory: ServiceNow APM tools allow organizations to capture comprehensive information about their applications, including metadata, dependencies, usage statistics, and support details.
Application Rationalization: ServiceNow APM tools enable organizations to assess their application portfolios and make informed decisions about retiring, replacing, or consolidating applications. They provide capabilities for analyzing application health, risk, cost, and alignment with business goals.
Collaboration: ServiceNow APM tools facilitate collaboration among different stakeholders by providing a single platform for capturing and sharing application information. This ensures that all stakeholders have access to up-to-date and accurate data.
Reporting and Analytics: ServiceNow APM tools offer advanced reporting and analytics capabilities that allow organizations to generate custom reports, visualize application portfolios, and gain insights into application performance and trends.
By leveraging ServiceNow APM tools, organizations can streamline their APM efforts, enhance collaboration among stakeholders, and make informed decisions about their application portfolios.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Enterprise Architecture Solutions
To understand the real-world impact of enterprise architecture Find more info solutions, let's take a look at some case studies:
Case Study 1: Company X
Challenge: Company X was struggling with inefficiencies in its IT infrastructure and operations. Different departments were using disparate systems that did not communicate effectively with each other.
Solution: Company X implemented an enterprise architecture solution that involved aligning its business processes with its IT capabilities. It developed a comprehensive business architecture that identified key business functions, processes, and dependencies. It also implemented an integrated technology architecture that standardized the IT infrastructure across departments.
Results: The enterprise architecture solution enabled Company X to streamline its operations, reduce costs associated with IT infrastructure maintenance, and improve collaboration among different departments. The organization experienced increased efficiency, better decision-making, and improved customer satisfaction.
Case Study 2: Company Y
Challenge: Company Y was facing challenges in managing its application portfolio. Many applications were outdated or redundant, resulting in higher maintenance costs and increased risk of security breaches.
Solution: Company Y implemented an application portfolio management (APM) solution that involved assessing the health and risk of its applications, identifying opportunities for rationalization, and making informed decisions about retiring or consolidating applications.
Results: The APM solution enabled Company Y to optimize its application portfolio, reduce maintenance costs, and mitigate security risks. The organization experienced improved agility, reduced complexity, and enhanced user satisfaction.
These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits that enterprise architecture solutions can bring to organizations. By aligning business goals with IT capabilities, organizations can achieve operational excellence, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Unlocking the Power of Enterprise Architecture: FAQs
What is enterprise architecture? Enterprise architecture is a strategic framework that helps organizations align their business objectives with their IT capabilities to achieve optimal performance and competitive advantage.
Why is enterprise architecture important? Enterprise architecture is important because it improves decision-making, drives innovation, enhances agility, reduces costs, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
What are the key components of enterprise architecture? The key components of enterprise architecture include business architecture, information architecture, application architecture, and technology architecture.
What are the benefits of adopting enterprise architecture? The benefits of adopting enterprise architecture include improved alignment, enhanced efficiency, effective decision-making, increased agility, better risk management, and improved collaboration.
What are the challenges in implementing enterprise architecture? Some common challenges in implementing enterprise architecture include lack of executive support, organizational silos, resistance to change, complexity, and lack of skills and expertise.
How can organizations ensure successful enterprise architecture adoption? Organizations can ensure successful enterprise architecture adoption by securing executive support, defining a clear vision and strategy, engaging stakeholders, starting small and scaling up, leveraging existing standards and frameworks, and continuously monitoring and adapting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, unlocking the power of enterprise architecture is crucial for organizations looking to achieve optimal performance and competitive advantage. By aligning business objectives with IT capabilities, enterprise architecture enables organizations to make informed decisions, drive innovation, enhance agility, and reduce costs.
The key to successful enterprise architecture adoption lies in securing executive support, engaging stakeholders, leveraging enterprise architecture tools, and following best practices. By doing so, organizations can unlock the full potential of their enterprise architecture initiatives and gain a strategic edge in today's fast-paced business world.
So embrace the power of enterprise architecture and embark on a journey towards success!